Migration From Ingress to Gateway API
Ingress offers a centralized approach for managing external access to services within a Kubernetes cluster, primarily handling HTTP/HTTPS traffic at Layer 7. Rather than assigning a dedicated load balancer to each service, Ingress provides a unified entry point for directing inbound requests to backend applications.
An Ingress resource specifies routing rules that determine how external traffic is forwarded to Kubernetes services. These rules can include hostnames, paths, and TLS settings. An Ingress controller then takes these configurations and applies them to the underlying data plane—such as a reverse proxy or load balancer—to actually serve the traffic.
Limitation
However, Ingress is limited to L7 HTTP/HTTPS. Support for other L7 protocols (like gRPC) or lower-layer protocols (such as TCP and UDP) requires custom controller extensions rather than native Ingress functionality. This creates fragmentation: essential capabilities like authentication, rate limiting, or advanced traffic policies depend on controller-specific annotations. For example, NGINX and HAProxy Ingress controllers each rely on their own custom syntax and extensions.
The Ingress specification also lacks built-in support for many advanced traffic management features expected in production environments. As a result, capabilities such as canary deployments, A/B testing, or distributed tracing become tightly tied to the vendor implementation instead of being portable across platforms. While Ingress focuses narrowly on basic HTTP routing, more sophisticated networking behaviors must be configured directly on the controller, adding complexity and reducing consistency across environments.
To solve the limitations around Kubernetes Ingress, the Gateway API project was created as an evolving standard to unify capabilities across different Ingress Controllers.
Gateway API defines a common set of Kubernetes resource objects and usage patterns that all compliant gateways must support.
Gateway API supports both L4 and L7 protocols including TCP, UDP, HTTP, gRPC, and more are under consideration. This expands its scope beyond just HTTP traffic.
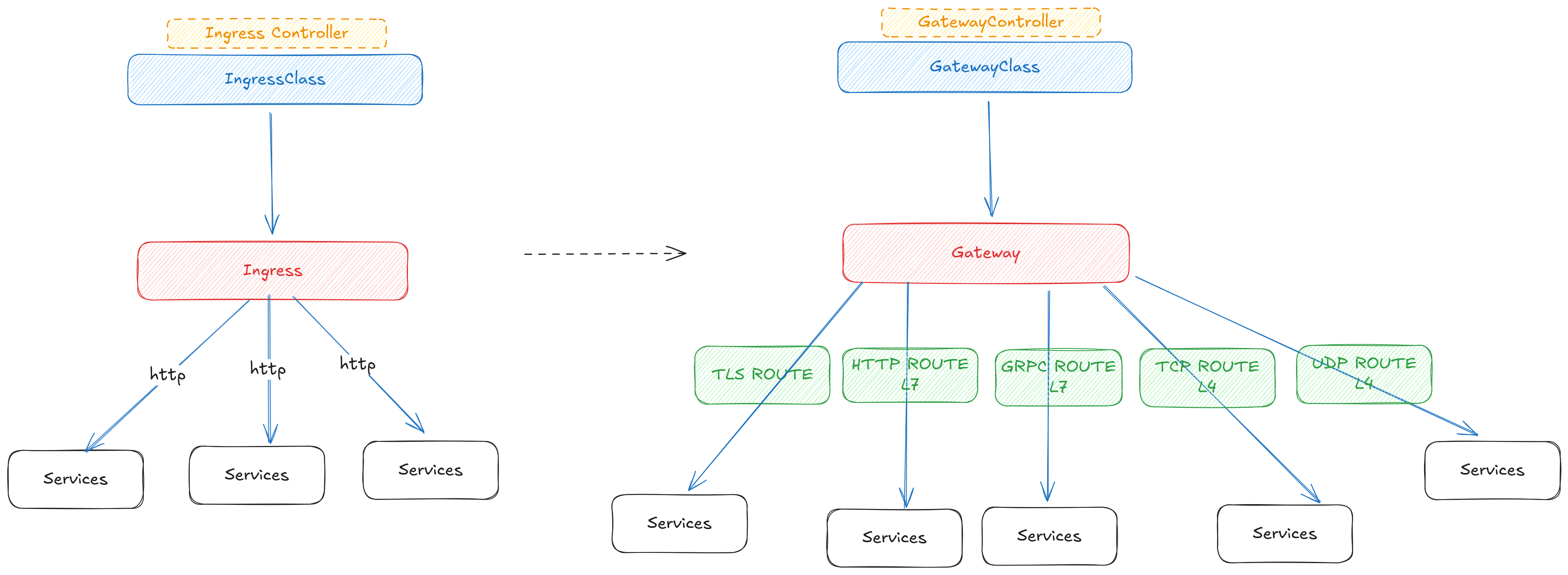
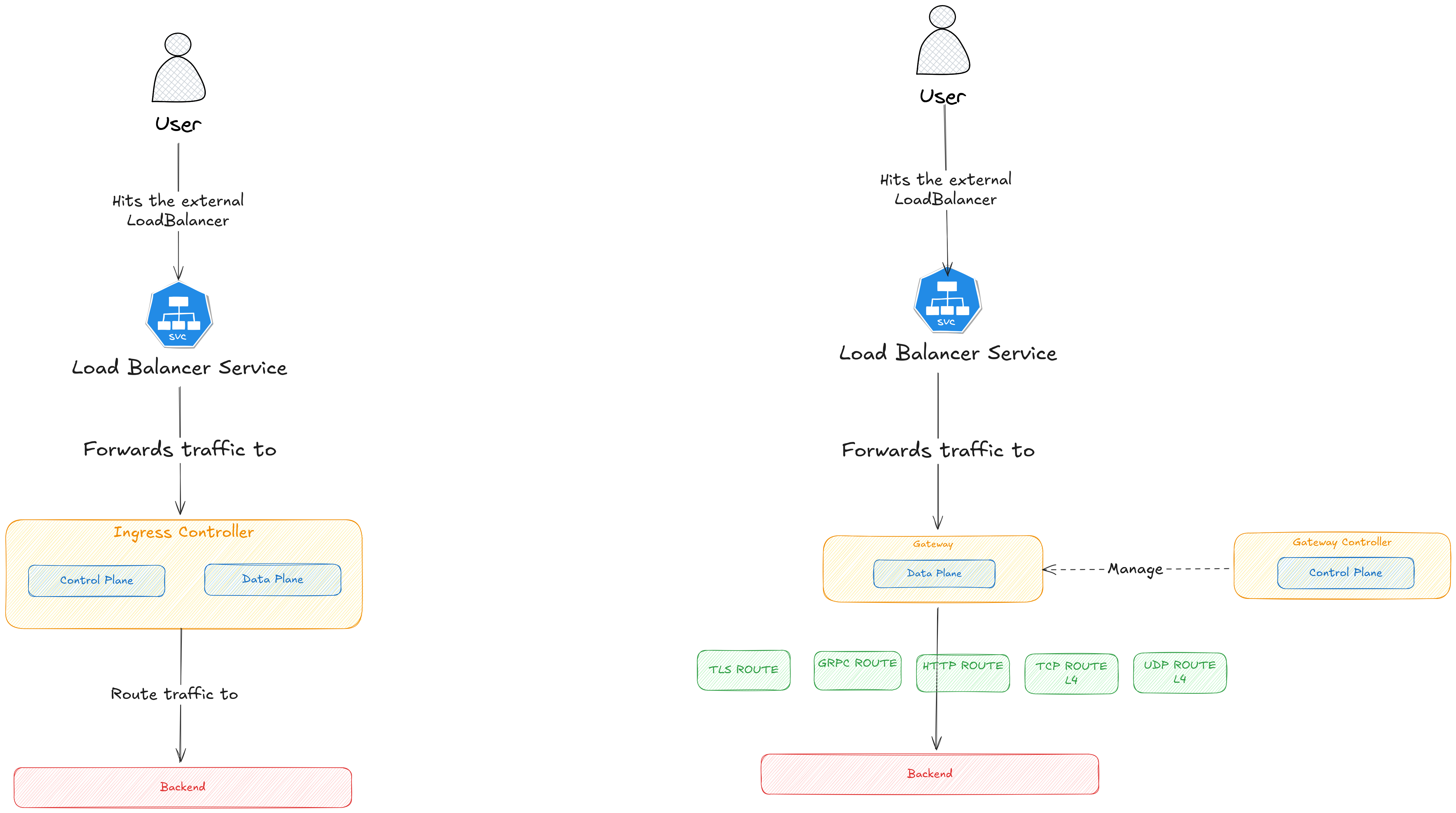
A key architectural difference between Ingress and Gateway API is how they structure the control plane and data plane.
1-Ingress Controller An Ingress Controller is a single component that combines both roles:
Control plane: Watches Ingress resources and translates rules
Data plane: The very same pods run NGINX, HAProxy, Traefik, etc. and serve traffic
After installation, the controller’s pods remain static. When you apply a new Ingress: No new data-plane pods are created The Ingress Controller simply updates its existing proxy configuration.
2-Gateway API
Gateway API deliberately separates the control plane from the data plane.
Control plane: The Gateway controller (e.g., Envoy Gateway) watches Gateway, Route, and policy resources.
Data plane: The controller creates dedicated proxy pods to handle traffic.
When you apply a Gateway:
✅ A new Deployment is created ✅ One or more Envoy proxy pods (or other proxies) are launched
Here is a list of several Gateway controllers

Overview
| Feature / Project | Cilium | Envoy Gateway | Istio | Kgateway | Kong | Traefik | Nginx |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Open Source | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ❌ (Since 3.10) | ✅ | ✅ |
| Open Source Foundation | CNCF | CNCF | CNCF | CNCF | No foundation | No foundation | No foundation |
| Enterprise Vendors (Support) | Single Vendor (Isovalent) | Single Vendor (Tetrate) | Many vendors | Single Vendor (solo.io) | Single Vendor (Kong) | Single Vendor (Traefik) | Single Vendor (F5) |
| Dataplane Proxy | Envoy | Envoy | Envoy | Envoy | Nginx | Traefik | Nginx |
Gateway API Has Two Types of APIs When working with Gateway API, you must distinguish between:
These are official Kubernetes APIs, fully standardized by the Gateway API project. They exist in the upstream API (same everywhere, same behavior).
Gateway API Standard Resources
| Standard API | Purpose |
|---|---|
GatewayClass |
Defines a type of Gateway implementation (Envoy, Kong, etc.) |
Gateway |
Represents a load balancer or entry point |
HTTPRoute / GRPCRoute / TLSRoute / TCPRoute / UDPRoute |
Provides routing rules for L7 and L4 traffic |
ReferenceGrant |
Enables cross-namespace reference permissions |
BackendTLSPolicy (emerging) |
Configures backend TLS settings |
While these resources define the standard surface of the Gateway API, not every gateway controller implements all of them, and some only offer partial or controller-specific support.
Gateway API Standard Resource Compatibility
| Gateway Controller | GatewayClass | Gateway | HTTPRoute | GRPCRoute | TLSRoute | TCPRoute | UDPRoute | ReferenceGrant | BackendTLSPolicy |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Envoy Gateway | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Cilium | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔ | ❌ |
| KGateway | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| Istio Gateway | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ (via HTTPRoute) | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
| NGINX Gateway Fabric | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | ✔ (Partially Supported) |
| Traefik | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ➖ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ | ✔ |
After identifying which controllers fully support the native Kubernetes Gateway API, we can now examine the extensions and proprietary APIs that each one introduces to provide additional capabilities.
Envoy Gateway API
| Resource | API | Required | Purpose | References | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backend | EG API | No | Routing | N/A | Used to route traffic to external backends (FQDN, IP) or processes exposed via Unix Domain Sockets. |
| BackendTrafficPolicy | EG API | No | Traffic Handling | Gateway, Route | Defines traffic management rules for backends: load balancing, health checks, failover. The most specific policy takes precedence. |
| ClientTrafficPolicy | EG API | No | Traffic Handling | Gateway | Defines policies for handling client traffic, such as rate limiting, retries, and timeouts. |
| SecurityPolicy | EG API | No | Security | Gateway, Route | Manages security settings: authentication, authorization, encryption. The most specific policy takes precedence. |
| EnvoyProxy | EG API | No | Customize & Extend | GatewayClass, Gateway | Represents and configures the Envoy proxy instance itself: deployment, scaling, resources, and bootstrap settings. |
| EnvoyPatchPolicy | EG API | No | Customize & Extend | GatewayClass, Gateway | Applies custom patches to Envoy Gateway/EnvoyProxy/XDS resources. The most specific patch wins. |
| EnvoyExtensionPolicy | EG API | No | Customize & Extend | Gateway, Route, Backend | Enables Envoy extensions: WASM, custom filters, and native extensions. The most specific policy wins. |
| HTTPRouteFilter | EG API | No | Customize & Extend | HTTPRoute | Allows defining additional request/response processing for HTTP routes. |
Cillium API
| Resource | API Group | Required | Purpose | References | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CiliumGatewayClassConfig | cilium.io/v2alpha1 | Optional | Configure how Cilium exposes Gateways created via a GatewayClass (Service type, IP families, LB behavior, source ranges, etc.) | Cilium docs – Gateway API & CiliumGatewayClassConfig | Alpha CRD used by the Cilium Gateway controller to define Service-level settings (LoadBalancer/NodePort, externalTrafficPolicy, IP families, loadBalancerSourceRanges, etc.) for Gateways associated with a given GatewayClass. |
Kgateway API
| Resource | API Group | Required | Purpose | References | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Backend | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | Routing | HTTPRoute (as backend reference) | Allows routing to external services such as hostnames, IPs, managed services, or Lambda functions. |
| BackendConfigPolicy | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | Backend Policies | Backend | Defines advanced backend-level configuration such as timeouts, retries, or custom load-balancing behavior. |
| DirectResponse | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | Traffic Handling | Gateway, HTTPRoute | Returns a custom HTTP response directly, without forwarding the request to a backend (status code + body). |
| GatewayExtension | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | External Extensions | Gateway, TrafficPolicy | Integrates external services (extAuth, rateLimit, extProc). Acts as a bridge between KGateway and external systems. |
| GatewayParameters | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | Gateway Bootstrap | Gateway | Configures the gateway proxy deployment: bootstrap, listener settings, and overrides for the default proxy template. |
| HTTPListenerPolicy | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | Listener Policies | Gateway | Applies policies to HTTP/HTTPS listeners, such as header transforms, logging, or listener-level configuration. |
| TrafficPolicy | gateway.kgateway.dev/v1alpha1 | No | Advanced Traffic Mgmt | HTTPRoute, GatewayListeners | Attaches advanced traffic management features: auth, rate limiting, transformations, logs, resiliency rules. |
Nginx Fabrik API
| Resource | API | Required | Purpose | References | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ClientSettingsPolicy | NGF API | No | Client Connection | Gateway, HTTPRoute, GRPCRoute | Configures connection behavior between clients and NGINX (timeouts, buffering, connection controls). |
| ObservabilityPolicy | NGF API | No | Observability | HTTPRoute, GRPCRoute | Defines tracing, logging, and metrics settings; attaches directly to routes. |
| UpstreamSettingsPolicy | NGF API | No | Upstream Connection | Service | Controls how NGINX connects to backend services—timeouts, retries, keepalives; supports merge operations. |
Istio Traffic Management APIs (Service-mesh)
| Resource | API | Required | Purpose | References | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| VirtualService | Istio API (CRD) | No | Traffic Routing | Gateway, DestinationRule | Defines routing rules for HTTP, TCP, and gRPC traffic. Supports canary, A/B testing, header-based routing, fault injection, timeouts, retries, etc. |
| DestinationRule | Istio API (CRD) | No | Traffic Policies | VirtualService | Defines policies for a service or subset: load balancing, circuit breakers, connection pools, TLS modes, subset definitions (v1, v2, etc.). |
| Gateway | Istio API (CRD) | No | Ingress/Egress Control | VirtualService | Configures L4–L6 properties for mesh ingress/egress (ports, TLS). Binds to VirtualService for L7 routing. |
| ServiceEntry | Istio API (CRD) | No | External Service Registry | VirtualService, DestinationRule | Adds external services to the mesh service registry. Enables routing, policies, and telemetry for APIs, VMs, or legacy infra outside the mesh. |
| Sidecar | Istio API (CRD) | No | Proxy Scope Definition | Workloads | Controls which services a sidecar proxy can reach and which inbound ports it handles. Used to optimize mesh performance and limit reachability. |
Migration Guide Introduction
This guide explains how to migrate from Ingress to any Gateway implementation. For demonstration purposes, we will use Envoy Gateway as the example, showcasing the setup both with and without ExternalDNS integration.
The environment will include the following components:
- Envoy configured as the
GatewayClass - ExternalDNS (Cloudflare provider) — and a variant of the setup without ExternalDNS
- Gateway API with Envoy Gateway
- Cert-manager with Gateway API support enabled
- Gateway and HTTPRoute configuration
This guide will demonstrate the full setup in two scenarios:
With ExternalDNS enabled (automatic DNS record management)
Without ExternalDNS (manual DNS management)
1. Install Gateway API Standard CRDs
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.4.0/standard-install.yaml
2. Install Envoy Gateway
helm install eg oci://docker.io/envoyproxy/gateway-helm \
--version v1.5.6 \
-n envoy-gateway-system \
--create-namespace
3. Install Envoy Gateway
Create the file gatewayclass.yaml:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
name: eg
spec:
controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller
4. Create Cloudflare API Token Secret
kubectl create secret generic cloudflare-api-key --from-literal=apiKey=YOUR_API_TOKEN
5. Install ExternalDNS (Cloudflare)
Create a values.yaml for ExternalDNS:
provider:
name: cloudflare
env:
- name: CF_API_TOKEN
valueFrom:
secretKeyRef:
name: cloudflare-api-key
key: apiKey
If you are using a different DNS provider, refer to the ExternalDNS documentation and update this configuration accordingly.
6. Install Cert-Manager (GatewayAPI enabled)
helm upgrade --install cert-manager oci://quay.io/jetstack/charts/cert-manager --namespace cert-manager \
--set config.apiVersion="controller.config.cert-manager.io/v1alpha1" \
--set config.kind="ControllerConfiguration" \
--set config.enableGatewayAPI=true
Or in values.yaml:
config:
apiVersion: controller.config.cert-manager.io/v1alpha1
kind: ControllerConfiguration
enableGatewayAPI: true
7. Create ACME Issuer (http01)
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: issuer-demo
namespace: default
spec:
acme:
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-gateway
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
solvers:
- http01:
gatewayHTTPRoute:
parentRefs:
- kind: Gateway
name: gateway-demo
namespace: default
this will depend on
- kind: Gateway
name: gateway-demo
namespace: default
8. Gateway Resource
Create gateway.yaml:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: gateway-demo
namespace: default
annotations:
cert-manager.io/issuer: issuer-demo
cert-manager.io/issuer-kind: Issuer
spec:
gatewayClassName: eg
listeners:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: HTTP
hostname: example.com
- name: https
port: 443
protocol: HTTPS
hostname: example.com
tls:
mode: Terminate
certificateRefs:
- name: demo-com-tls
9. HTTPRoute Resource
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: http-route-demo
namespace: default
annotations:
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/cloudflare-proxied: "true"
external-dns.alpha.kubernetes.io/ttl: "300"
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: gateway-demo
sectionName: https
namespace: default
hostnames:
- example.com
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: backend-demo
port: 80
You may now access: example.com
Setup gateway without exteralDNS
1. Install Gateway API Standard CRDs
kubectl apply -f https://github.com/kubernetes-sigs/gateway-api/releases/download/v1.4.0/standard-install.yaml
2. Install Envoy Gateway
helm install eg oci://docker.io/envoyproxy/gateway-helm \
--version v1.5.6 \
-n envoy-gateway-system \
--create-namespace
3. Install Envoy Gateway
Create the file gatewayclass.yaml:
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: GatewayClass
metadata:
name: eg
spec:
controllerName: gateway.envoyproxy.io/gatewayclass-controller
4. Create ACME Issuer (http01)
apiVersion: cert-manager.io/v1
kind: Issuer
metadata:
name: issuer-demo
namespace: default
spec:
acme:
privateKeySecretRef:
name: letsencrypt-gateway
server: https://acme-v02.api.letsencrypt.org/directory
solvers:
- http01:
gatewayHTTPRoute:
parentRefs:
- kind: Gateway
name: gateway-demo
namespace: default
this will depend on
- kind: Gateway
name: gateway-demo
namespace: default
5. Gateway (initial minimal configuration)
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Gateway
metadata:
name: gateway-demo
namespace: default
spec:
gatewayClassName: eg
listeners:
- name: http
port: 80
protocol: HTTP
6. HTTPRoute (initial minimal configuration)
apiVersion: gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: HTTPRoute
metadata:
name: http-route-demo
namespace: default
spec:
parentRefs:
- name: gateway-demo
sectionName: https
namespace: default
hostnames:
- example.com
rules:
- matches:
- path:
type: PathPrefix
value: /
backendRefs:
- name: backend-demo
port: 80
7.Retrieve Gateway IP
kubectl get gateway gateway-demo -n envoy-gateway-system -o jsonpath='{.status.addresses[0].value}'
Create your record with this ip .
8. Patch Gateway for HTTPS + Certificate
kubectl patch gateway gateway-demo -n cattle-system --type merge -p '{
"metadata": {
"annotations": {
"cert-manager.io/issuer": "issuer-demo",
"cert-manager.io/issuer-kind": "Issuer"
}
},
"spec": {
"listeners": [
{
"name": "http",
"protocol": "HTTP",
"port": 80,
"hostname": "example.com"
},
{
"name": "https",
"protocol": "HTTPS",
"port": 443,
"hostname": "example.com",
"tls": {
"mode": "Terminate",
"certificateRefs": [
{
"name": "demo-com-tls"
}
]
}
}
]
}
}'